You may be aware of the expression “A lazy man will always find an easier way”*. I first heard it from a custodian where I was working nights to raise money for university. One dinner break he explained his method for achieving 8 hours of work in 4 on the night shift. He had devised a system of optimizing speed while limiting the total number of footsteps required to clean 12 classrooms an evening.

I won’t detail his method here but I will say it was far better thought out than a few high-tech startup ideas I have been pitched. In this context of efficiency we can consider that “lazy” refers to a person who seeks to avoid effort or exertion by finding shortcuts or easier methods.
The statement can also be hailed as a testament to the entrepreneurial spirit emphasizing the pursuit of efficiency and optimization. History is replete with instances where individuals, driven by a desire to minimize effort, have sparked innovation and transformed industries.
Examining Efficiency through the Lens of Innovation
Take, for example, the advent of assembly line production pioneered by Henry Ford. Ford was inspired by the meat-packing houses of Chicago and a grain mill conveyor belt he had seen. If he brought the work to the workers, they spent less time moving about.
It’s an interesting perspective to consider how certain traits, like what some may perceive as “laziness,” can play a role in someone’s success. In the case of Henry Ford, it’s not necessarily that he was lazy in the conventional sense, but rather that he was known for his desire to find easier and more efficient ways of doing things.
Ford famously said, “I believe that the average farmer puts to a really useful purpose only about 5% of the energy he expends. Not only is everything done by hand, but seldom is a thought given to a logical arrangement.”
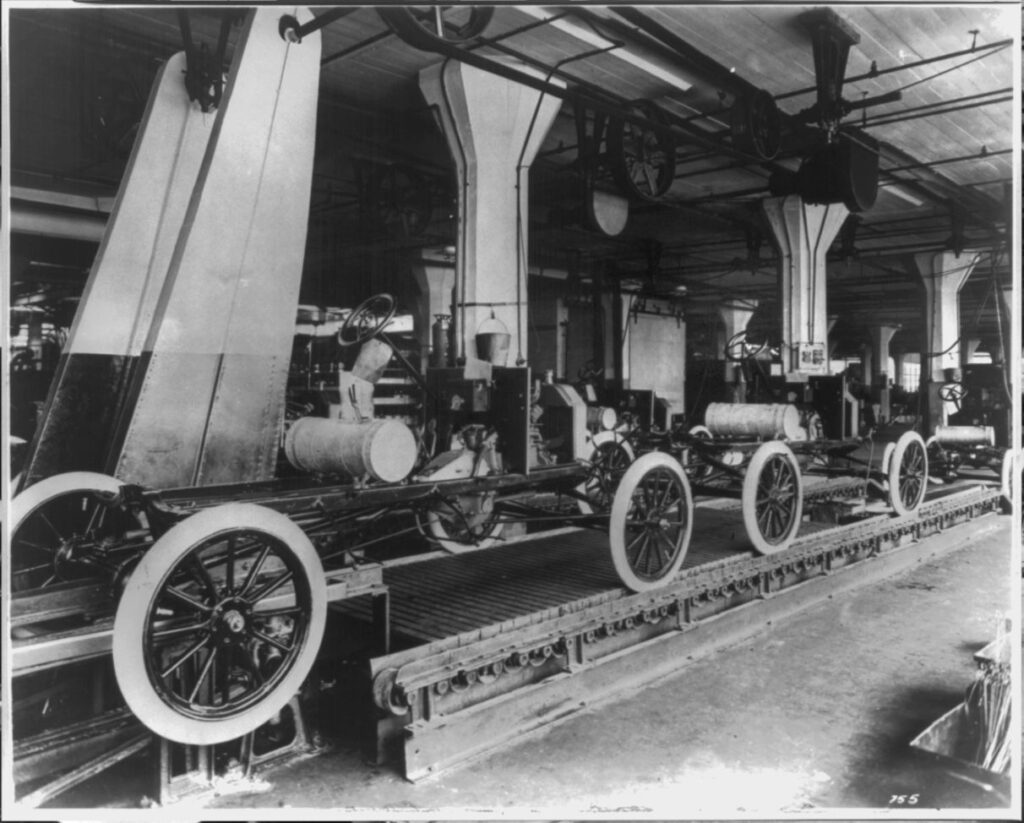
No offense to our Mr. Ford but working farms tend to be pretty well thought out. This sentiment does however clearly reflect Ford’s disdain for inefficiency and his drive to streamline processes.
By streamlining the manufacturing process, Ford not only revolutionized the automotive industry but also exemplified how laziness, when channeled effectively, can lead to remarkable advancements in productivity and profitability.
A cautionary tale…
On the flip side, however, the notion that laziness inherently leads to innovation warrants scrutiny. While it’s true that seeking shortcuts can spur creativity, it can also breed complacency and undermine quality.

Consider the case of Theranos, the health technology startup company founded by Elizabeth Holmes. Driven by the desire to revolutionize blood testing, Holmes embarked on an ambitious journey to simplify the process, but the challenge of raising substantial funds intensified the pressure, pushing her to deliver results in an increasingly high-stakes environment.

In the end her relentless pursuit of a shortcut, and failure to heed the feedback of the Chief Scientist, led to fraudulent practices and ultimately the downfall of the company, it’s investors, and Holmes. This cautionary tale underscores the importance of distinguishing between the concepts of constructive laziness that drives innovation and reckless laziness that invites disaster.
It’s essential to recognize that not all shortcuts are created equal.
While the concept of “finding an easier way” can indeed catalyze innovation, it’s essential to recognize that not all shortcuts are created equal. In the dynamic landscape of business, embracing “laziness” as a catalyst for efficiency requires a nuanced approach. It demands a balance between recognizing opportunities for optimization and maintaining a steadfast commitment to quality and integrity.

Using Ford’s assembly line as a starting point we will dissect seven core elements across three categories; the “Lesson” learned from Ford’s experience, a “Modern Challenge” faced today, and finally how the “Application” of AI to the challenge provides a solution.
1. Efficiency and Scalability:
- Lesson: The assembly line allowed Ford to produce cars faster and at a lower cost by breaking down the production process into smaller, repeatable tasks.
- Modern Challenge: Today, businesses face the challenge of increasing workflow efficiency while maintaining a healthy work-life balance for employees.
- Application: AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) can assist businesses in automating repetitive tasks, streamlining processes, and improving decision-making. For example, AI can handle routine customer service inquiries, allowing human employees to focus on more complex and creative tasks. This not only increases productivity but also respects the human need for meaningful work, contributing to a better quality of life and a healthier, more productive workforce. By leveraging AI responsibly, companies can scale their operations without compromising employee well-being.
2. Standardization:
- Lesson: Ford standardized parts and processes, enabling the production of large quantities of cars with consistent quality, which also simplified repairs and maintenance for consumers.
- Modern Challenge: In today’s fast-paced environment, businesses must maintain consistent quality across their offerings while adapting to rapid changes in technology and customer expectations.
- Application: AI and LLMs can help standardize business processes such as data entry, document management, and content creation, ensuring consistency and accuracy across all outputs. For instance, an AI-driven content management system can automatically format and proofread documents, reducing errors and maintaining a high standard of quality. At the same time, these tools can be configured to allow for flexibility and creativity where needed, ensuring that the human touch remains integral to the business.
3. Customer-Centric Innovation:
- Lesson: The assembly line made cars affordable to the average American, transforming them from luxury items into necessities by focusing on making products accessible to a broader market.
- Modern Challenge: Companies today need to innovate in ways that resonate with diverse customer bases, often with varying needs and preferences, while maintaining inclusivity and accessibility.
- Application: AI and LLMs can analyze vast amounts of customer data to identify trends and preferences, enabling businesses to tailor products and services to meet specific market demands. For example, personalized AI-driven marketing campaigns can ensure that different customer segments receive relevant offers and communications. This approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also promotes inclusivity, ensuring that products and services are accessible to all, regardless of background or ability.
4. Iterative Improvement:
- Lesson: Ford continually refined the assembly line process, improving efficiency, reducing waste, and lowering costs through an iterative approach.
- Modern Challenge: Businesses today must constantly innovate and improve to stay competitive in a rapidly changing market, all while managing the potential burnout of employees from continuous change.
- Application: AI and LLMs can facilitate iterative improvement by providing real-time analytics and feedback, helping businesses refine their strategies and products more effectively. For example, AI can monitor production processes and suggest optimizations, reducing waste and improving quality over time. Importantly, these tools can be designed to support employee workflows, offering suggestions without overwhelming workers, thereby promoting sustainable innovation that considers both efficiency and employee well-being.
5. Cost Reduction and Affordability:
- Lesson: The assembly line drastically reduced the cost of producing cars, allowing Ford to lower prices and make the Model T affordable for the masses.
- Modern Challenge: Today, companies must find ways to reduce costs without compromising on quality, while also addressing the growing demand for ethical and sustainable business practices.
- Application: AI and LLMs can help reduce costs by optimizing supply chain management, reducing energy consumption, and predicting maintenance needs. For instance, AI-driven predictive maintenance can lower the costs associated with equipment failure, ensuring that operations run smoothly and resources are used efficiently. By integrating AI in ways that also promote sustainable practices, businesses can reduce costs while maintaining a commitment to ethical production, ultimately making high-quality products more affordable and accessible.
6. Labor Specialization and Team Efficiency:
- Lesson: By assigning workers to specific tasks, Ford improved productivity and reduced the time needed for training, maximizing efficiency.
- Modern Challenge: Businesses today must balance the need for specialized roles with the need for employees to feel engaged and valued in their work, avoiding the pitfalls of repetitive or monotonous tasks.
- Application: AI and LLMs can take over repetitive or mundane tasks, allowing employees to focus on more complex, specialized work that requires human creativity and problem-solving. For example, AI can handle data processing or routine administrative tasks, freeing up employees to engage in strategic planning or creative endeavors. This not only improves overall team efficiency but also enhances job satisfaction by allowing workers to focus on areas where they can make the most meaningful contributions.
7. Vision and Long-Term Thinking:
- Lesson: Ford’s vision extended beyond simply building cars; he aimed to make them accessible to the general public, a long-term strategy that drove his success.
- Modern Challenge: Companies today must develop long-term strategies that balance innovation, market demands, and sustainability, all while navigating the complexities of a globalized economy.
- Application: AI and LLMs can assist in long-term strategic planning by analyzing market trends, predicting future scenarios, and providing insights into emerging opportunities. For instance, AI can model the potential impact of different business strategies over time, helping leaders make informed decisions that align with both short-term goals and long-term visions. By leveraging AI to support strategic decision-making, companies can ensure that their vision is both innovative and sustainable, taking into account the well-being of all stakeholders involved.
Let’s review three examples where this concept was embraced successfully at Amazon, Google and :

1. Amazon’s One-Click Ordering
Scenario: Jeff Bezos, inspired by the idea of minimizing customer effort, sought to reduce the friction in the purchasing process.
Outcome: Amazon developed the “One-Click” ordering system, which allows customers to purchase items with a single click, bypassing the traditional multi-step checkout process. This simplification not only improved the customer experience but also increased conversion rates and sales by removing barriers to purchase.

2. Google’s Search Algorithm
Scenario: Google co-founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin recognized that users were spending too much time sifting through irrelevant search results.
Outcome: Google developed an advanced search algorithm that prioritizes the most relevant results based on user queries and browsing history. This innovation significantly reduced the time and effort users needed to find information, making the search process faster and more efficient.

3. CallMiner’s Automated Customer Service Chatbots
CallMiner is the Leader in the Forrester Wave™: Conversation Intelligence for Customer Service, Q3 2023
Scenario: Companies faced increasing volumes of customer service inquiries, leading to inefficiencies and high operational costs.
Outcome: Many businesses adopted automated customer service chatbots to handle routine queries and tasks. These chatbots reduce the need for human intervention in repetitive scenarios, thereby streamlining customer service operations, reducing response times, and allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues.
With business efficiency leveraging breakthroughs in AI, a lazy person will find an easier way!
With efficiency increasingly’ leveraging breakthroughs in AI, a lazy person will inevitably find an easier way—often through a bit of creative disruption.

What might initially appear as a “lazy” approach has, time and again, sparked significant improvements in efficiency and user satisfaction. By embracing this unconventional mindset, organizations can tap into the power of simplicity, automation, and even a touch of disorder, to drive meaningful, innovative improvements. Maybe lazy thinking is exactly what’s needed to shake things up, try a new perspective and achieve smarter, more effective solutions.
*Title updated to reflect change in common language.