Claude’s coordinated minds compared to Google’s free-thinking agents
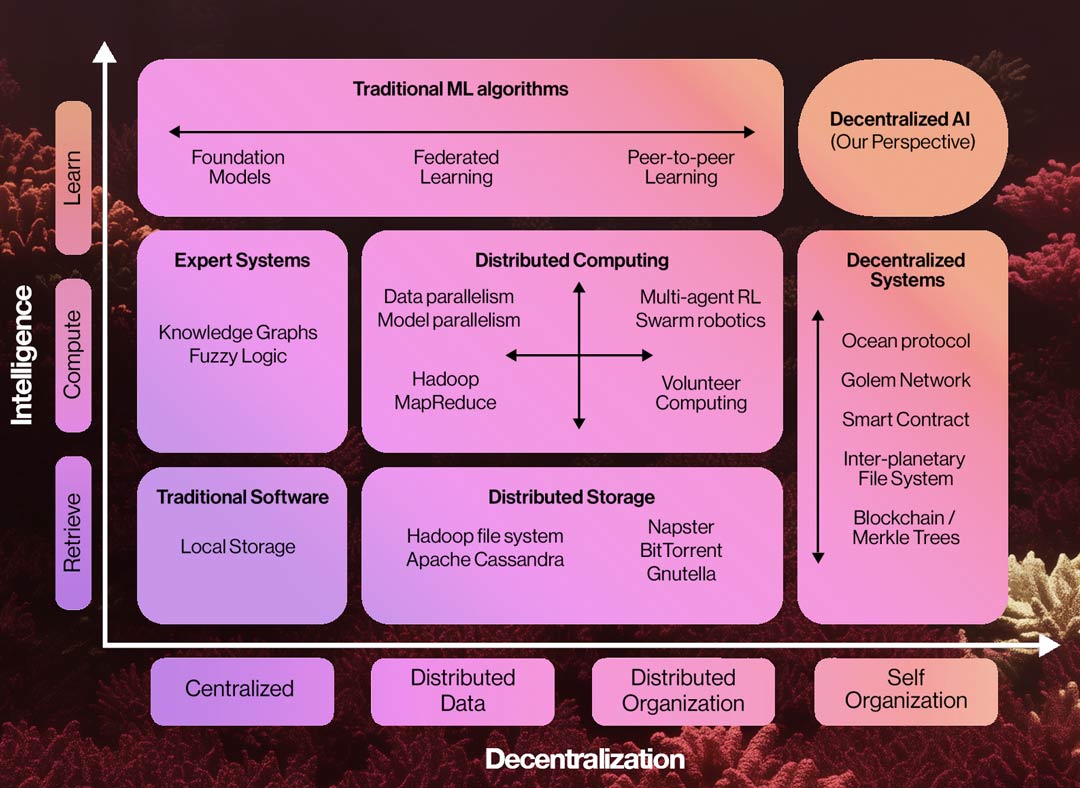
As artificial intelligence evolves from monolithic models to modular, multi-agent ecosystems, two distinct coordination philosophies are emerging – each backed by a leading AI innovator.
Google’s Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol
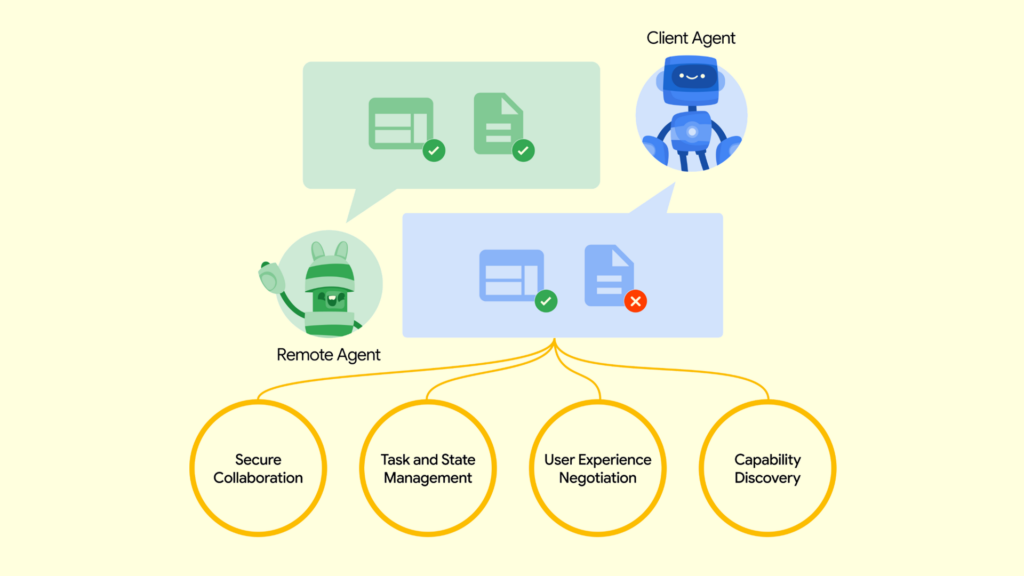
Google’s A2A protocol is a pioneering framework that enables independent AI agents to communicate, delegate tasks, and reason together dynamically. Built for scale and flexibility, it supports emergent, collaborative intelligence – where specialized agents work together like an adaptive digital team. It’s Google’s blueprint for distributed cognitive systems, aiming to unlock the next frontier of AI-driven autonomy and problem-solving.
Claude’s Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Anthropic’s MCP takes a different approach. It enables Claude to safely coordinate sub-agents under tightly governed rules and ethical constraints. Task decomposition, execution, and reintegration are centrally managed – ensuring outputs remain reliable, aligned, and auditable. Rooted in Anthropic’s “Constitutional AI” philosophy, MCP prioritizes trust and transparency over autonomy.
Two Visions, One Destination
While both protocols seek to advance multi-agent systems, their contrasting designs reflect broader strategic trade-offs:
- A2A favors creative autonomy and scalability.
- MCP emphasizes governance, safety, and alignment.
Enterprises evaluating AI strategy must understand these paradigms – not just as technical choices, but as directional bets on how intelligence should be organized, managed, and trusted in mission-critical environments.
Everyman Metaphor
Google A2A is like a team of smart coworkers in a brainstorming session.
- Each one jumps in when they have something to add.
- They chat, debate, hand off work.
- The A2A protocol is their shared meeting rules so no one talks over anyone else, and ideas flow.
Claude MCP is like a project manager assigning tasks to freelancers with checklists.
- Each sub-agent has a clear role and safety constraints.
- Claude ensures alignment, checks results, and approves before anything ships.
- MCP is the project charter + checklist system that keeps things on track and ethical.
Why This Matters to a CEO
1. Different Models of Intelligence
- A2A (Google): Builds toward emergent, distributed problem-solving – good for R&D, dynamic workflows, and creative automation.
- MCP (Claude): Optimized for safe, auditable, structured outputs – great for legal, financial, or sensitive business processes.
2. Innovation vs Control
- A2A allows for fast exploration across agents.
- MCP ensures high reliability and governance in outputs.
3. Strategic Advantage
- Choosing the right model can define your org’s AI maturity and risk posture.
- A2A is agile and experimental. MCP is compliant and dependable.

Elevator Pitch (AI Strategy Lens):
We’re seeing two AI philosophies crystalize. Google’s A2A Protocol is about autonomous AI agents reasoning and working together – modular intelligence at scale. Anthropic’s Claude MCP is a more structured approach, where sub-agents are coordinated safely and transparently under alignment protocols. A2A is the future of creative, emergent AI systems; MCP is the foundation for trustworthy AI in sensitive, high-stakes environments. The real unlock? Enterprises will need both – creativity where it’s safe, and constraint where it’s critical.
| Feature | Google A2A | Claude MCP (Anthropic) |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Autonomous agents reasoning together | Managed coordination for safe, aligned outcomes |
| Style of Collaboration | Open-ended, agent-initiated delegation | Controlled, system-managed orchestration |
| Use Case Example | One agent researches, another writes, a third validates facts | Claude delegates parts of a legal doc to specialized agents for summary, tone, and risk-check |
| Agent Autonomy | High — agents reason and request help | Moderate – agents act under system-defined guardrails |
| Trust & Alignment Focus | Flexible reasoning, goal-directed | Guardrails, safety, constitutional AI principles |
| Goal | Scalable collective intelligence | Trustworthy coordination of AI-driven tasks |
Claude’s Managed Coordination Protocol (MCP)
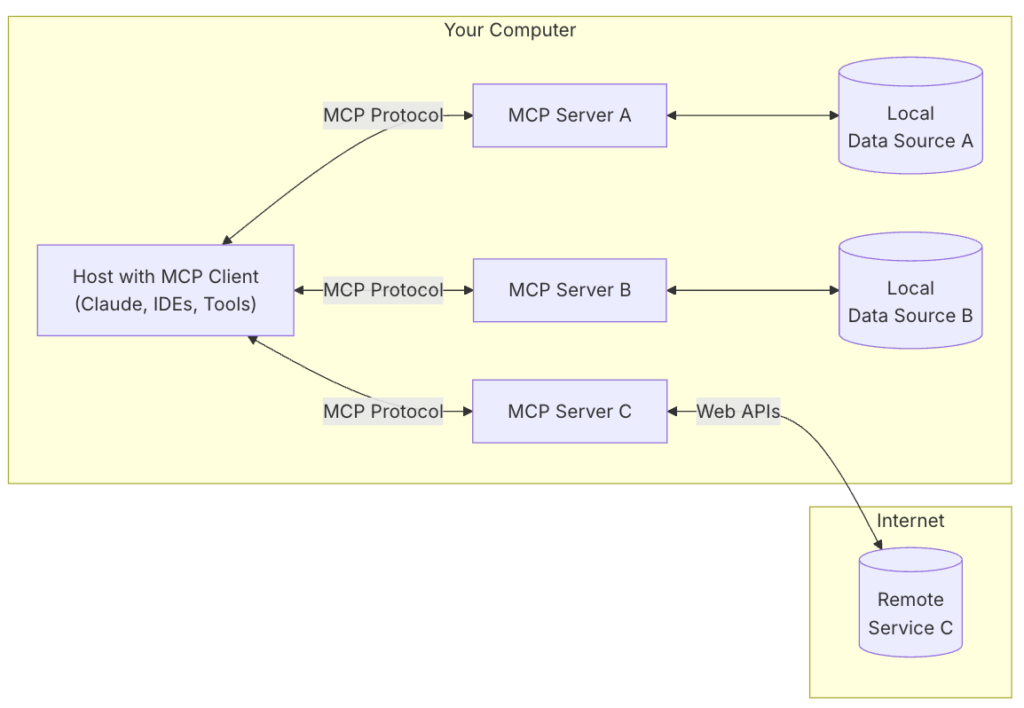
Google’s Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol
SOURCE:
A2A:
Dev Document
MCP:
Dev Document