The reality of AI Influencers in Marketing
It is no surprise that artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping industries across the globe. One of the most intriguing developments in this realm is the emergence of AI influencers—digital personas driven by sophisticated algorithms, designed to engage with audiences in much the same way as human influencers.

These AI figures are not just marketing tools, they are also creating new possibilities for brands to connect with their audiences, offering a fresh take on digital influence and marketing. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the concept of AI influencers, taking a closer look at two high-profile examples in the fashion and sports sectors: Laila, the AI influencer created for Puma Morocco, and Maya Puma, the collaboration between IPG Mediabrands and Puma. We’ll also explore why these AI personalities matter for businesses and how they can play a key role in your marketing strategy.

The Rise of AI Influencers
AI influencers are digital entities that use artificial intelligence and machine learning to interact with human audiences through social media platforms, advertising campaigns, and branded content. Unlike human influencers, AI influencers are entirely virtual—they are created from a combination of machine learning, image recognition, and data analysis, which allows them to respond to trends, audience feedback, and cultural shifts with remarkable precision.

The attraction of AI influencers lies in their ability to remain “always on”—24/7 engagement, no sleep, no off-days. They are immune to controversies or scandals that can derail a human influencer’s career. Additionally, AI influencers can be designed to embody ideal brand traits and values, offering brands a chance to craft the perfect ambassador for their products.
In many ways, these AI personalities represent the next frontier in digital marketing, offering a new level of personalization, reliability, and scalability. But how do these digital avatars work, and how can brands leverage them to maximize their reach?
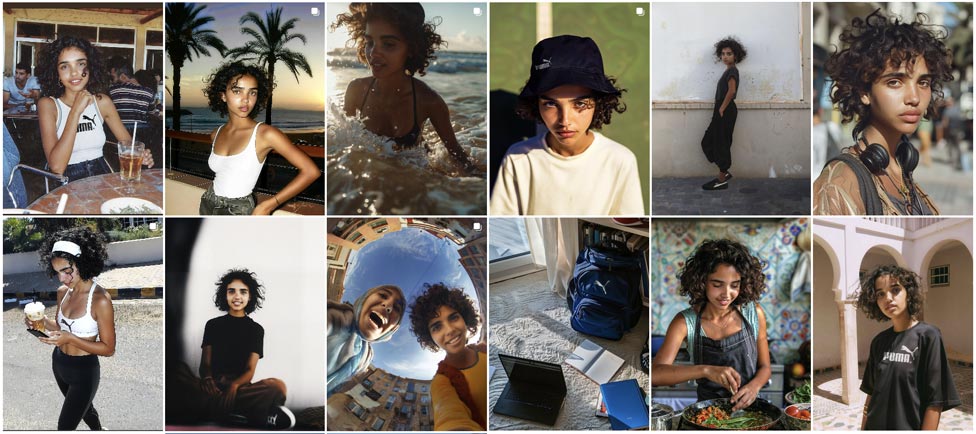
Puma Morocco’s AI Influencer Laila
In 2022, Puma Morocco launched Laila, an AI influencer designed to blend seamlessly into the digital fabric of Morocco’s fashion scene. The idea behind Laila was to create a virtual ambassador who felt human, yet was distinctly not, by combining local cultural nuances with the global appeal of Puma.

What makes Laila so interesting is her ability to present herself as a relatable and “real” figure, despite being an entirely virtual creation. As the team behind her explains, Laila was not made to seem “too artificial”—she is, in fact, deeply humanized. The brand used her as an interactive tool in Puma’s social media and digital marketing campaigns, generating buzz with her appearances in photoshoots, engagement with fans, and promotion of the latest collections.
Laila was designed to resonate with Morocco’s youth, embodying style, inclusivity, and empowerment, key attributes that Puma wanted to highlight in their messaging. As a result, the AI influencer garnered significant attention for Puma in the region, engaging fans on a new level and helping the brand deepen its connection with the Moroccan market.
The OG AI Influencer Maya by IPG Mediabrands
Back in 2020, Puma and IPG Mediabrands took a bold leap into the future of influencer marketing with the creation of Maya, one of the first AI-powered influencers designed to promote Puma’s products to a global audience. Maya was groundbreaking for its time, a digital persona that pushed the boundaries of what AI could do in the fashion world. With a focus on Puma’s core values—performance, innovation, and inclusivity—Maya was designed to engage audiences in fresh ways while also making a strong statement about how AI could bridge the gap between technology and fashion.
At the time, Maya’s blend of machine learning and AI-powered responses to followers was cutting-edge. She responded to comments, stayed on top of trends, and interacted with Puma’s audience through dynamic content pieces that showcased the brand’s products in innovative and authentic ways. Maya was not simply a virtual model; she was an evolving character, interacting with fans and participating in a conversation about the future of AI in fashion.
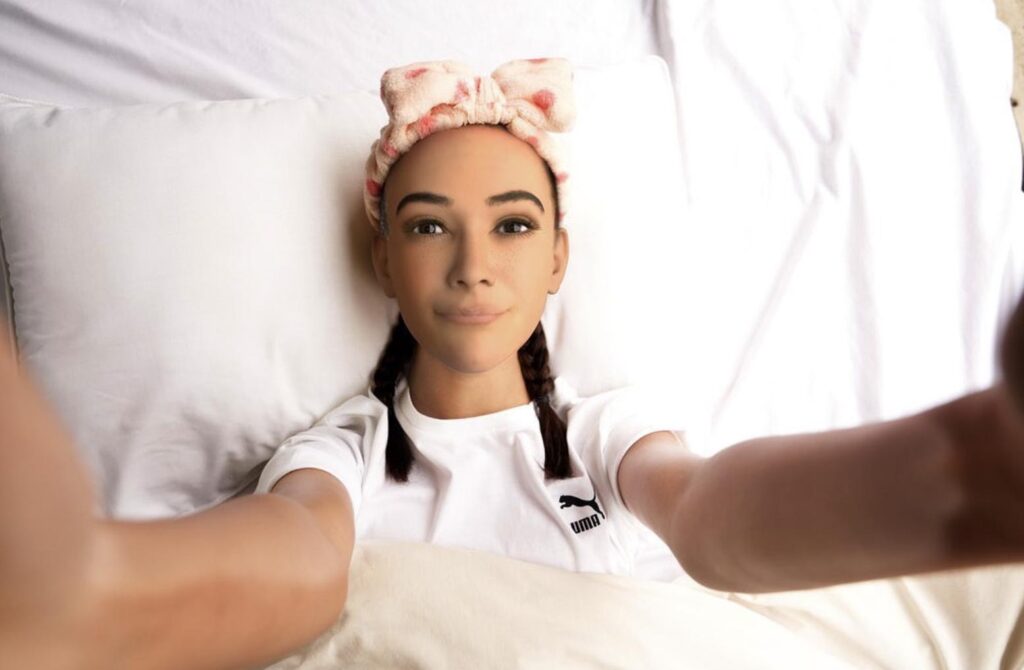

However, looking back now, Maya’s design seems almost quaint in comparison to the more advanced AI influencers of today. While Maya’s digital persona helped pave the way for AI personalities in marketing, the technology available in 2020 was still in its early stages. Maya’s interactions were fairly scripted, and her appearance, though advanced at the time, did not have the same level of realism or fluidity seen in more recent AI influencers like Laila.
What set Maya apart was her role in sparking a conversation about the place of AI in the fashion and marketing industries. She wasn’t just a tool for selling products—she was part of a broader cultural dialogue. Through collaborations, virtual interviews, and her own evolving “brand,” Maya embodied the beginning of a shift in how digital personas could engage audiences, but today, her technology feels like a stepping stone to the more sophisticated, lifelike AI influencers that have followed.
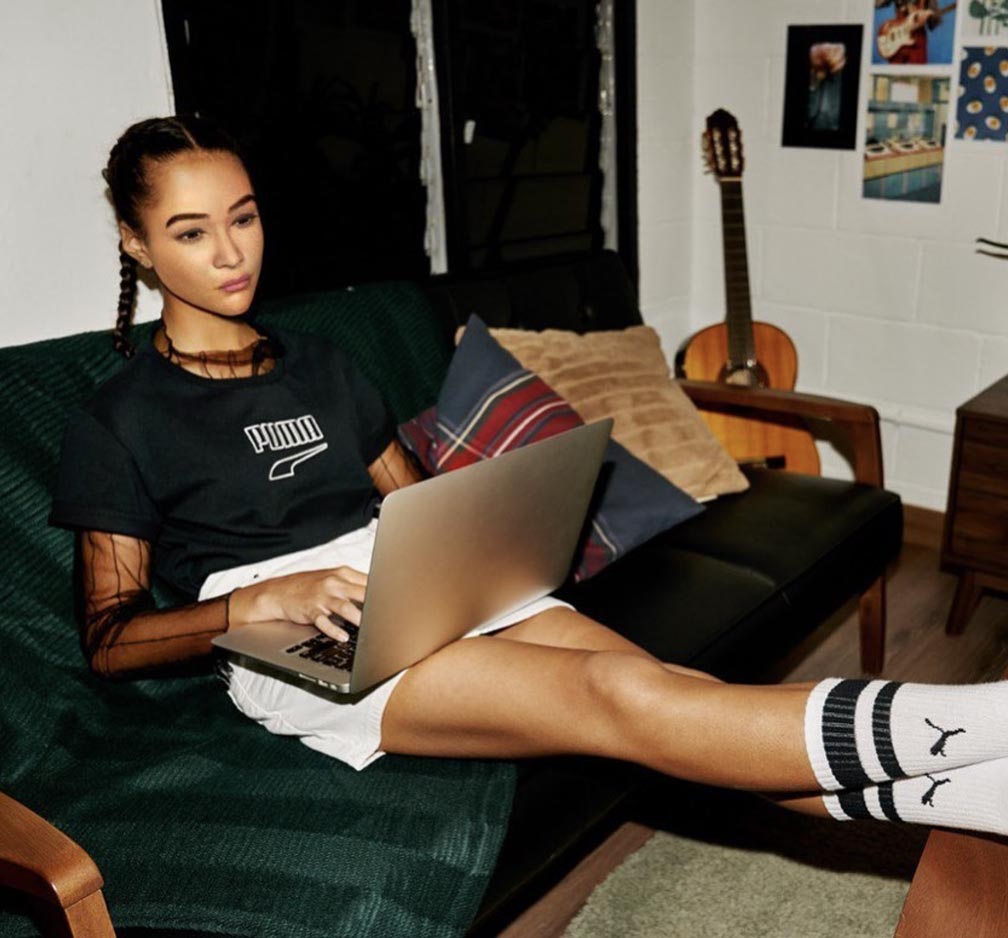

Despite this, Maya’s presence was pivotal in showing the world what was possible at the time and served as a benchmark for the AI influencers that would come after her. Her legacy lies in her pioneering role, opening the door to a new wave of digital personalities that continue to redefine what it means to be an “influencer” in the digital age.
Why AI Influencers Matter to a CEO
CEOs should care about AI influencers because they represent an evolution in digital marketing and customer engagement that can help brands scale, personalize, and maintain relevance in an increasingly digital world. As customer expectations shift towards more personalized experiences, AI influencers offer a unique way to fulfill those demands at a fraction of the cost and risk associated with traditional human influencers.
Moreover, AI influencers can be programmed to embody a brand’s ethos in ways that human influencers cannot always maintain. They can be optimized to handle high-volume interactions, offer always-on availability, and remain completely brand-aligned, avoiding the unpredictable nature of human behavior.
For CEOs seeking ways to increase ROI on digital marketing campaigns, or to carve out new avenues for growth in emerging markets, the rise of AI influencers is a compelling option. They provide a clear advantage in terms of cost-effectiveness, scalability, and brand control.
Core Value Proposition of AI Influencers
The core value proposition of AI influencers is their ability to offer brands a scalable, cost-effective, and hyper-personalized marketing solution that aligns perfectly with the digital-first world we live in. By leveraging the precision of artificial intelligence, AI influencers can seamlessly engage with target audiences, build meaningful relationships, and stay perfectly aligned with brand values—all while remaining immune to the uncertainties and risks that human influencers bring to the table.
Key Value Propositions:
- Personalized Engagement: AI influencers can analyze data to craft tailored messages that resonate deeply with an individual’s preferences, behaviors, and emotional triggers. This level of personalization drives higher engagement and conversion rates.
- Brand Consistency & Control: Unlike human influencers who may experience fluctuations in their behavior, AI influencers are fully programmable to embody the brand’s ethos, ensuring complete alignment with the company’s values, tone, and messaging.
- Scalability & Availability: AI influencers are always on, never requiring breaks or vacation time. This 24/7 engagement allows brands to maintain constant interaction with consumers across time zones and at scale—something human influencers can’t match.
- Cost-Effectiveness: With AI influencers, there’s no need for expensive celebrity endorsements or the risks associated with human influencers’ erratic behaviors. They can be “deployed” at a fraction of the cost, while maintaining high engagement.
Primer: Enabling Technology Behind AI Influencers
The creation and success of AI influencers are driven by a combination of several advanced technologies, each playing a critical role in the ability of these digital avatars to influence and engage with audiences. Here are the core technologies that enable AI influencers to exist and perform effectively:
Cloud computing provides the infrastructure needed to handle the massive amounts of data that AI influencers interact with daily. By using cloud platforms, AI influencers can process real-time data, access large-scale training datasets, and continuously update their behavior and appearance.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning:
AI enables influencers to learn from vast amounts of data and adapt to changing trends, user behaviors, and interactions. Machine learning algorithms analyze engagement patterns and audience sentiment, helping AI influencers generate more effective content.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows AI influencers to engage in meaningful and contextually aware conversations with followers, giving them the ability to respond to comments, queries, and mentions with an understanding of human language nuances.
Computer Vision & Deep Learning:
Computer vision technology allows AI influencers to “see” the world through visual recognition systems. This is essential for creating realistic, human-like appearances, and enabling them to interact with visual content like photos and videos.
Deep learning algorithms help AI influencers improve over time by interpreting complex data—everything from human emotions to visual aesthetics—making them more relatable and “authentic.”
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs):
GANs are crucial for creating realistic images and videos of AI influencers. These networks consist of two neural networks—one generating content (the generator) and the other evaluating it (the discriminator)—which improves the visual quality of the AI character over time.
GANs help AI influencers appear lifelike, making them more engaging and relatable to audiences.
Synthetic Media & Digital Human Creation:
Using synthetic media, AI influencers can be created as fully virtual personas that appear in videos, photoshoots, and other digital media. This allows brands to create personalized avatars that resonate with specific target markets.
Digital human creation technology involves crafting AI-driven characters that mimic human behavior, facial expressions, and body language, all while retaining complete control over the digital persona.
Social Media Automation Tools:
AI influencers are empowered by social media automation technologies that allow them to manage and optimize interactions on platforms like Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok. These tools help AI influencers post content, reply to comments, and stay engaged with their audience automatically, ensuring a seamless experience.
Elevator Pitch: Adding AI Influencers to a MarCom Plan
Imagine a digital ambassador for your brand that works around the clock, never gets sick, and can interact with your customers in a personalized, meaningful way. That’s what an AI influencer offers. From generating authentic engagement to showcasing your products in creative, cutting-edge ways, AI influencers bring a unique blend of innovation, consistency, and precision to your marketing communications. Whether you’re looking to increase brand awareness, build deeper connections with consumers, or tap into new markets, AI influencers are an indispensable tool in your marketing arsenal.

BLACK HAT BEATDOWN – WARNING THIS IS EXPERIMENTAL
TRUST NOTHING. LOVE NOTHING. AGREE WITH NOTHING UNTIL IT SURVIVES A BEATING.
Alright, let’s tear this Elevator Pitch apart like it’s a bad alibi at a crime scene. First off, AI influencers? Really? Let me break this down, because we’re already knee-deep in fantasy land.
- Authenticity? Sure, you’re calling it “authentic engagement” like it’s the next holy grail. But authenticity requires human flaws—imperfection. Real people screw up, show vulnerability, and have stories that are hard to replicate, even with advanced algorithms. Your AI influencer is what? A programmed parrot? It doesn’t live, breathe, or feel. And consumers—especially now—are smart enough to sniff out a plastic smile from a mile away. If they feel like they’re being sold by a bot, they’re gone. End of story.
- Consistency? Consistency is a trap. Consistency breeds stagnation. It’s like trying to turn a serial killer into a law-abiding citizen by giving them a routine. People love the unpredictable, the surprising. AI might pump out content every hour, but it’ll be the same damn thing every time, almost like your brand’s trying to beat the same dead horse. Guess what? Consumers hate repeating themselves—especially when it’s the same old pre-packaged content.
- “Building Connections”? Have you ever tried connecting with a toaster? Same thing. AI doesn’t have real experiences or genuine emotions, so it can’t actually connect with people. You think it’s going to emotionally engage someone just because it can “talk” to them? Newsflash: it doesn’t feel, it doesn’t grow, it doesn’t care. It’s a well-dressed algorithm with a pre-scripted persona. How is that deeper than a poorly executed sales pitch?
Here’s the harsh reality: brands need real human touch, not digital puppets. The second your customers realize they’re chatting with a bot instead of a person, you’ve lost. It’s a crutch that brands are using to hide their inability to build actual, human-driven relationships. This isn’t innovation; it’s desperation wrapped in a digital disguise.

SOURCE: